Evaluating geroprotective interventions using in vivo medical imaging
We aim to develop biomarkers and new treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. We do this by applying medical imaging techniques, such as MRI, PET and CT, to pre-clinical models of neurodegeneration, as well as human patients. Currently, we are running an academically sponsored phase IIa trial in early Alzheimer’s disease, where we assess the effect of the drug sirolimus (a.k.a. rapamycin) on neurodegeneration, brain metabolism and aging processes.
Our work also involves developing and validating biomarkers of aging that can be used as endpoints in clinical trials of geroprotective compounds. To this end, we apply machine learning models to large batches of multi-modal imaging data to estimate the biological age of different organ-systems in the human body.
ERAP
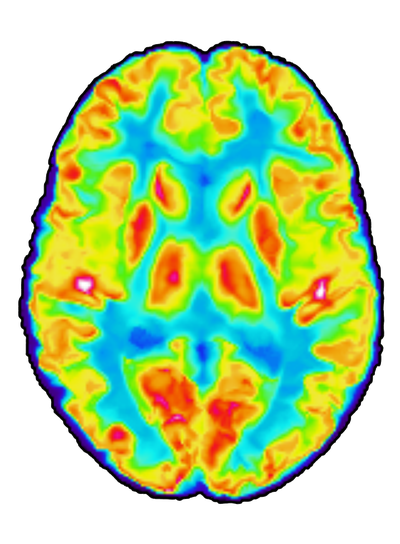
"Evaluating Rapamycin in Alzheimer's disease using Positron emission tomography" (or ERAP for short) is a clinical phase IIa pilot trial. In this one-arm, open-label trial, we assess if the drug rapamycin/sirolimus can be repurposed as a treatment for dementia disorders and neurodegeneration.
The trial is a collaboration between Karolinska Institutet and the Karolinska Hospital Memory Clinic in Solna, Sweden. It was initiated on September 1, 2023, and patients with early-stage Alzheimer's disease or mild cognitive impairment are currently being enrolled by invitation. Participants are treated for six months with a weekly dose of 7 mg sirolimus. Before and at the end of the treatment, all participants undergo a series of examinations where we quantify the change in cerebral glucose metabolism, cerebral blood flow, disease-markers in the CSF and cognition.
In addition, all participants are examined with a set of medical imaging techniques to quatify change in heart function, bone and muscle density, retinal nerve layer thickness, as well as atherosclerotic- and periodontal inflammation. The purpose of these examinations is to assess if rapamycin affects age-related pathological processes in organs and tissues also outside the central nervous system.
clinicaltrials.gov ID: NCT06022068